Coverer Setup and Management
Overview
This guide provides detailed instructions for setting up and managing coverers in Out of Office Assistant. Coverers are colleagues who automatically receive issue assignments when you’re away from work, ensuring continuous project progress and customer service.
Understanding Coverer Functionality
What Are Coverers?
Coverers are team members who:
Automatically receive issues assigned to you during your absence
Handle responsibilities on your behalf to maintain project continuity
Can be individual users or groups of users for load distribution
Must have appropriate permissions in target projects
Coverer Assignment Process
When your absence rule is active:
Issue Detection: New issues assigned to you are identified
Coverer Selection: System selects appropriate coverer based on configuration
Assignment Transfer: Issue automatically reassigned to selected coverer
Notification: Coverer receives standard Jira assignment notification
Comment Addition: Optional out-of-office message posted to issue
Types of Coverer Configurations
Single Coverer: One person handles all your issues during absence
Multiple Coverers: Round-robin distribution among several team members
Approval Coverer: Specialized for Jira Service Management approval workflows
Single Coverer Setup
When to Use Single Coverer
Best Scenarios:
Short absences (1–3 days)
Specialized roles requiring specific expertise
Small teams with clear backup arrangements
Projects with low issue volume
Considerations:
Verify coverer availability during entire absence period
Ensure coverer has capacity to handle additional workload
Confirm coverer expertise matches your role responsibilities
Configuring Single Coverer
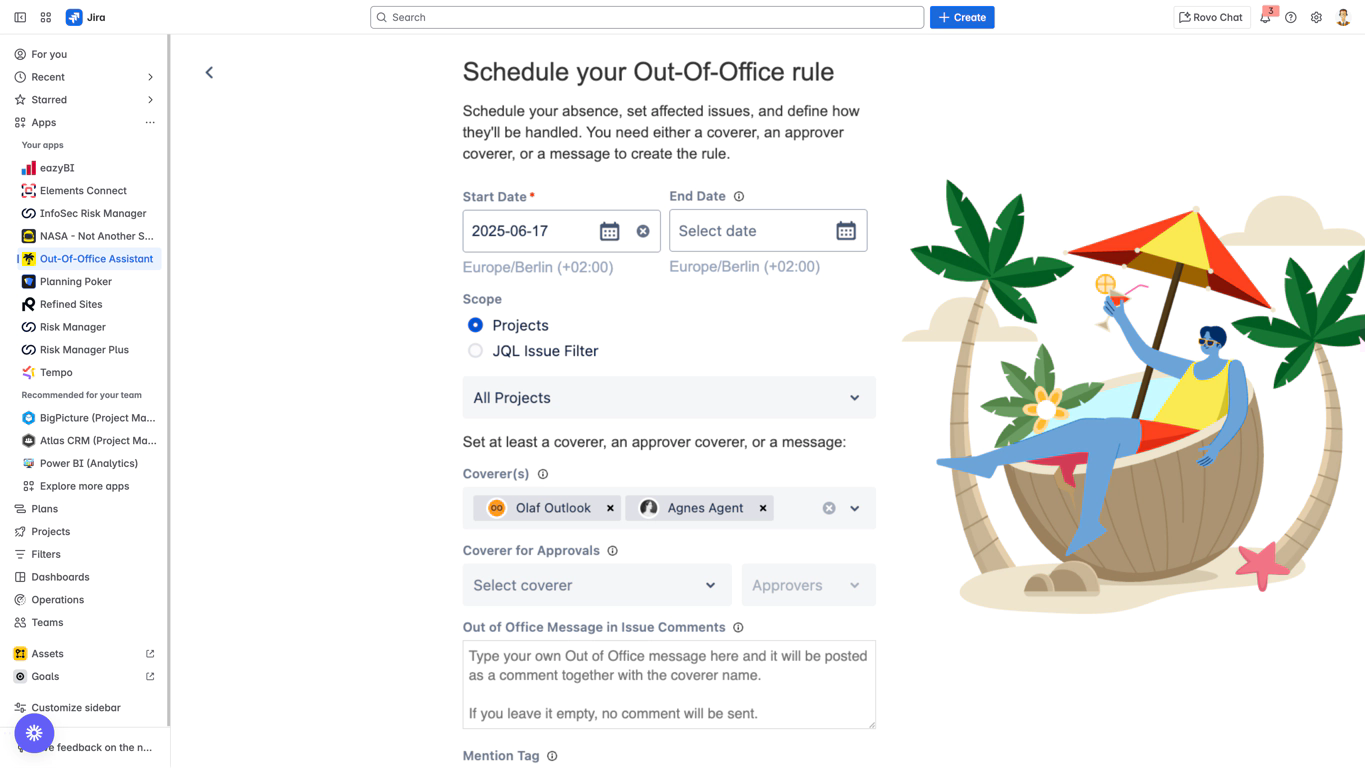
Step 1: Access Coverer Configuration
Open rule creation form (Apps → Out-Of-Office Assistant → Add rule for myself)
Navigate to “Coverer(s)” section in the form
Verify field label shows “Who will cover your tasks”
Step 2: Select Your Coverer
Click the “Coverer(s)” dropdown field
Type colleague’s name - dropdown filters dynamically as you type
Select user from filtered dropdown results
Verify selection appears in the field
Step 3: Validate Coverer Choice
Permission Check: Ensure coverer can be assigned issues in your projects
Availability Verification: Confirm coverer is available during your absence
Capacity Assessment: Verify coverer can handle additional workload
Expertise Match: Ensure coverer has skills for your issue types
Single Coverer Example Configuration:
- Coverer(s): John Smith
- Projects: All Projects
- Message: I'm out of office until [date]. John Smith will handle my assignments.
Single Coverer Best Practices
Coverer Selection Criteria:
Project Access: Must have assignment permissions in all relevant projects
Role Compatibility: Should have similar skills and responsibilities
Availability: Confirmed availability during entire absence period
Communication: Established working relationship and communication channels
Pre-Absence Coordination:
Brief Coverer: Provide context on current issues and priorities
Share Resources: Provide access to relevant documentation and tools
Set Expectations: Clarify decision-making authority and escalation paths
Contact Information: Ensure coverer has emergency contact details
Multiple Coverer Setup
When to Use Multiple Coverers
Ideal Scenarios:
Extended absences (1 week or longer)
High-volume issue environments
Load balancing across team members
Redundancy for business continuity
Benefits:
Load Distribution: Prevents overwhelming single person
Expertise Diversification: Leverages different skills across team
Availability Insurance: Backup if one coverer becomes unavailable
Fair Workload: Distributes responsibility equitably
Round-Robin Functionality
How Round-Robin Works:
Issue Assignment: First issue goes to Coverer #1
Next Assignment: Second issue goes to Coverer #2
Rotation Continues: Third issue goes to Coverer #3 (or back to #1 if only 2 coverers)
Fair Distribution: System maintains balanced assignment counts
Round-Robin Algorithm:
Sequential Assignment: Issues assigned in order of coverer list
Automatic Cycling: System tracks assignment counts for balance
No Manual Intervention: Distribution happens automatically
Configuring Multiple Coverers
Step 1: Add First Coverer
Click “Coverer(s)” dropdown
Type first colleague’s name
Select from dropdown when name appears
Verify first coverer appears in field
Step 2: Add Additional Coverers
Click dropdown again to add second coverer
Type second colleague’s name
Select from dropdown results
Repeat process for additional coverers (up to practical limit)
Step 3: Verify Coverer List
Review all selected coverers in the field
Confirm order (first selected = first in rotation)
Check permissions for all coverers in target projects
Validate availability for all coverers during absence
Multiple Coverer Example Configuration:
- Coverer(s): Alice Johnson, Bob Wilson, Carol Martinez
- Distribution: Round-robin assignment
- Projects: All Projects
- Message: I'm out of office until [date]. Issues will be distributed among Alice, Bob, and Carol.
Multiple Coverer Best Practices
Team Selection Strategy:
Skill Diversity: Include coverers with complementary expertise
Availability Staggering: Choose team members with different schedules
Experience Levels: Mix senior and junior team members for mentoring
Project Knowledge: Select team members familiar with your projects
Load Balancing Considerations:
Current Workload: Account for each coverer’s existing responsibilities
Capacity Planning: Ensure combined team can handle your issue volume
Peak Times: Consider business cycles and expected issue patterns
Backup Plans: Identify additional coverers if primary team unavailable
Coordination Requirements:
Team Meeting: Brief entire coverer team together
Communication Channels: Establish team communication for coordination
Escalation Process: Define process for complex issues requiring consultation
Knowledge Sharing: Create shared resources accessible to all coverers
Approval Coverer Configuration
Understanding Approval Delegation
Purpose: Specialized coverer configuration for Jira Service Management (JSM) projects
Function: Delegates approval decisions to coverers during absence
Scope: Applies specifically to approval workflows in JSM projects
When Approval Delegation Is Needed:
You have approval responsibilities in JSM projects
Customer requests require approval during your absence
Service level agreements must be maintained
Approval bottlenecks must be prevented
JSM Approval Workflow Integration
Standard JSM Approval Process:
Customer Request: Submitted through service portal
Approval Required: Workflow pauses for approval decision
Approval Assignment: Normally assigned to you for decision
During Absence: Automatically delegated to approval coverer
Decision Making: Approval coverer makes approval decision
Workflow Continuation: Process continues based on approval outcome
Configuring Approval Coverers
Step 1: Access Approval Configuration
Navigate to “Coverer for Approvals” section in rule form
Identify JSM projects where you have approval responsibilities
Verify approval workflow requirements for each project
Step 2: Select Approval Coverer
Click “Select coverer” dropdown in Coverer for Approvals section
Type approval coverer’s name
Select from dropdown results
Verify coverer selection appears in field
Approval Coverer Example Configuration:
- Coverer for Approvals: Sarah Thompson (Project Manager)
- Approvers: Michael Chen (Team Lead)
- Projects: Customer Support Portal, IT Service Desk
Restrictions
JQL-based rules for approvers are not supported.
Groups of approvers cannot be utilized.
Only one approver coverer is permitted.
Modifications to the workflows that manage the approval processes may prevent the app from delegating approvals for existing issues that entered the approval process prior to the most recent workflow change.
Approval Coverer Requirements
Permission Prerequisites:
JSM Project Access: Must have agent or administrator access
Approval Authority: Must have approval permissions in workflow
Customer Interaction: Should have customer communication skills
Business Knowledge: Must understand approval criteria and policies
Training Requirements:
Approval Criteria: Understanding of when to approve/reject requests
Escalation Procedures: Knowledge of when to escalate complex decisions
Customer Communication: Skills for professional customer interaction
SLA Awareness: Understanding of service level commitments
Coverer Management Status: ✅ COMPLETE
Next Step: Rule Configuration Guide
